Search for answers or browse our Knowledge Base.
Guides | Models | Validation | Book
-
Guides
-
-
- New Tools in AN-SOF: Selecting and Editing Wires in Bulk
- How to Speed Up Simulations in AN-SOF: Tips for Faster Results
- Enhancing Antenna Design Flexibility: Project Merging in AN-SOF
- AN-SOF Antenna Simulation Best Practices: Checking and Correcting Model Errors
- How to Adjust the Radiation Pattern Reference Point for Better Visualization
-
- Can AI Design Antennas? Lessons from a 3-Iteration Yagi-Uda Experiment
- Modeling Common-Mode Currents in Coaxial Cables: A Hybrid Approach
- Beyond Analytical Formulas: Accurate Coil Inductance Calculation with AN-SOF
- Complete Workflow: Modeling, Feeding, and Tuning a 20m Band Dipole Antenna
- DIY Helix High Gain Directional Antenna: From Simulation to 3D Printing
- Design Guidelines for Skeleton Slot Antennas: A Simulation-Driven Approach
- Linking Log-Periodic Antenna Elements Using Transmission Lines
- An Efficient Approach to Simulating Radiating Towers for Broadcasting Applications
- AN-SOF Mastery: Adding Elevated Radials Quickly
- Fast Modeling of a Monopole Supported by a Broadcast Tower
- RF Techniques: Implicit Modeling and Equivalent Circuits for Baluns
-
- Understanding the Antenna Near Field: Key Concepts Every Ham Radio Operator Should Know
- Evaluating EMF Compliance - Part 1: A Guide to Far-Field RF Exposure Assessments
- Evaluating EMF Compliance - Part 2: Using Near-Field Calculations to Determine Exclusion Zones
- Wave Matching Coefficient: Defining the Practical Near-Far Field Boundary
- AN-SOF Data Export: A Guide to Streamlining Your Workflow
- Front-to-Rear and Front-to-Back Ratios: Applying Key Antenna Directivity Metrics
- Exporting Radiation Patterns to MSI Planet Format: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Exporting Radiation Patterns to Radio Mobile: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Generating Field Isocontours: Integrating AN-SOF with Scilab
-
-
-
- Introducing AN-SOF 10.5 – Smarter Tools, Faster Workflow, Greater Precision
- Introducing the AN-SOF Engine: Power, Speed, and Flexibility for Antenna Simulation
- What’s New in AN-SOF 10? Smarter Tools for RF Professionals and Antenna Enthusiasts
- To Our Valued AN-SOF Customers and Users: Reflections, Milestones, and Future Plans
- AN-SOF 9.50 Release: Streamlining Polarization, Geometry, and EMF Calculations
- AN-SOF 9: Taking Antenna Design Further with New Feeder and Tuner Calculators
- AN-SOF Antenna Simulation Software - Version 8.90 Release Notes
- AN-SOF 8.70: Enhancing Your Antenna Design Journey
- Introducing AN-SOF 8.50: Enhanced Antenna Design & Simulation Software
- Get Ready for the Next Level of Antenna Design: AN-SOF 8.50 is Coming Soon!
- Explore the Cutting-Edge World of AN-SOF Antenna Simulation Software!
- Upgrade to AN-SOF 8.20 - Unleash Your Potential
- AN-SOF 8: Elevating Antenna Simulation to the Next Level
- New Release: AN-SOF 7.90
- AN-SOF 7.80 is ready!
- New AN-SOF User Guide
- New Release: AN-SOF 7.50
- AN-SOF 7.20 is ready!
- New Release :: AN-SOF 7.10 ::
- AN-SOF 7.0 is Here!
- New Release :: AN-SOF 6.40 ::
- New Release :: AN-SOF 6.20 ::
- Show All Articles (7) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Types of Wires
- Wire Attributes
- Wire Materials
- Enabling/Disabling Resistivity
- Enabling/Disabling Coating
- Cross-Section Equivalent Radius
- Exporting Wires
-
-
Models
-
- Download Example Models
- Explore 5 Antenna Models with Less Than 50 Segments in AN-SOF Trial Version
- Modeling a Center-Fed Cylindrical Antenna with AN-SOF
- Modeling a Circular Loop Antenna in AN-SOF: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Monopole Antennas Over Imperfect Ground: Modeling and Analysis with AN-SOF
- Modeling Helix Antennas in Axial Radiation Mode Using AN-SOF
- Step-by-Step: Modeling Basic Yagi-Uda Arrays for Beginners
-
- Modeling an Inverted V Antenna for 40 Meters: Design Insights and Ground Effects
- Modeling a Super J-Pole: A Look Inside a 5-Element Collinear Antenna
- The 5-in-1 J-Pole Antenna Solution for Multiband Communications
- Simulating a Multiband Omnidirectional Dipole Antenna Design
- The Loop on Ground (LoG) Antenna: A Compact Solution for Directional Reception
- Precision Simulations with AN-SOF for Magnetic Loop Antennas
- Advantages of AN-SOF for Simulating 433 MHz Spring Helical Antennas for ISM & LoRa Applications
- Understanding the Folded Dipole: Structure, Impedance, and Simulation
- Experimenting with Half-Wave Square Loops: Simulation and Practical Insights
- Radar Cross Section and Reception Characteristics of a Passive Loop Antenna: A Simulation Study
- Design and Simulation of Short Top-Loaded Monopole Antennas for LF and MF Bands
-
- Efficient NOAA Satellite Signal Reception with the Quadrifilar Helix Antenna
- Simulating Helical Antennas over Finite Wire-Grid Ground Planes
- Introduction to Yagi-Uda Arrays: Analyzing a 5-Element Beam with a Folded Dipole Driver
- Explicit Modeling of a 9-Element LPDA: Capturing Real-World Wideband Performance
- Exploring an HF Log-Periodic Sawtooth Array: Insights from Geometry to Simulation
- Boosting Performance with Dual V Antennas: A Practical Design and Simulation
-
- The Lazy-H Antenna: A 10-Meter Band Design Guide
- Extended Double Zepp (EDZ): A Phased Array Solution for Directional Antenna Applications
- Transmission Line Feeding in Antenna Design: Exploring the Four-Square Array
- Enhancing VHF Performance: The Dual Reflector Moxon Antenna for 145 MHz
- Building a Compact High-Performance UHF Array with AN-SOF: A 4-Element Biquad Design
- Building a Beam: Modeling a 5-Element 2m Band Quad Array
- A Closer Look at the HF Skeleton Slot Antenna
- The 17m Band 2-Element Delta Loop Beam: A Compact, High-Gain Antenna for DX Enthusiasts
- The Moxon-Yagi Dual-Band VHF/UHF Antenna for Superior Satellite Link Performance
-
- Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antennas: A Comparative Analysis of Transmission Line Theory and AN-SOF Numerical Results
- High-Performance Impedance Matching in Microstrip Antennas: The Role of Capacitive Feeding
- Simplified Modeling of Microstrip Antennas on Ungrounded Dielectric Substrates: A Practical First-Order Approach
- A Simple, Low-Cost Approach to Simulating Solid Wheel Antennas at 2.4 GHz
-
- Nelder-Mead Optimization for Antenna Design Using the AN-SOF Engine and Scilab
- Evolving Better Antennas: A Genetic Algorithm Optimizer Using AN-SOF and Scilab
- Building Effective Cost Functions for Antenna Optimization: Weighting, Normalization, and Trade-offs
- Element Spacing Simulation Script for Yagi-Uda Antennas
- Automating 2-Element Quad Array Design: Scripting and Bulk Processing in AN-SOF
-
-
Validation
-
- The AN-SOF Calculation Engine
- Electric Field Integral Equation
- The Exact Kernel
- The Method of Moments
- Excitation of the Structure
- Curved vs. Straight Segments
-
- Navigating the Numerical Landscape: Choosing the Right Antenna Simulation Method
- Overcoming 7 Limitations in Antenna Design: Introducing AN-SOF's Conformal Method of Moments
- Beyond NEC: Accurate LF/MF Grounding with the James R. Wait Model
- Validating Numerical Methods: Transmission Line Theory and AN-SOF Modeling
- Circuit Theory Validation: Simulating an RLC Series Resonator
-
- Validation of a Panel RBS Antenna with Dipole Radiators against IEC 62232 Standard
- Linear Antenna Theory: Historical Approximations and Numerical Validation
- Simple Dual Band Vertical Dipole for the 2m and 70cm Bands
- Validating V Antennas: Directivity Analysis with AN-SOF
- Validating Dipole Antenna Simulations: A Comparative Study with King-Middleton
- Energy Conservation and Gain Convergence in Cylindrical Dipoles: A Numerical Validation Study
- Numerical Convergence and Stability of Input Impedance in Cylindrical Dipoles
- Advanced Modeling of Monopoles over Radial Wire Ground Screens
-
- Precision Modeling of Small Loop Antennas: Validating the Conformal Method of Moments (CMoM)
- Input Impedance and Directivity of Large Circular Loops: Theory vs. Numerical Simulation
- Helical Antennas in Normal Mode: Theoretical Limits and Numerical Validation
- Validating AN-SOF Simulations for Gain and VSWR of Helix Antennas in Axial Mode
-
-
Book
-
- 1.0 Table of Contents
- 1.1 Maxwell’s Equations and Electromagnetic Radiation
- 1.2 The Isotropic Radiator
- 1.3 Arrays of Point Sources
- 1.4 The Hertzian Dipole – FREE SAMPLE
- 1.5 The Short Dipole
- 1.6 The Half-Wave Dipole
- 1.7 Thin Dipoles of Arbitrary Length
- 1.8 Ground Plane and Image Theory
- 1.9 Monopole Antennas
-
- 2.1 Radiation Pattern Fundamentals
- 2.2 Polarization
- 2.3 Radiated Power and Energy Conservation
- 2.4 Radiation Resistance
- 2.5 Radiation Efficiency
- 2.6 Directivity and Gain
- 2.7 Beamwidth and Sidelobes
- 2.8 Feedpoint Impedance and Bandwidth
- 2.9 The Reciprocity Principle
- 2.10 Receiving Mode Operation
- 2.11 Effective Aperture and Gain
- 2.12 The Friis Transmission Equation
-
Enhancing Antenna Design Flexibility: Project Merging in AN-SOF
Discover how AN-SOF’s project merging feature enhances antenna design flexibility by seamlessly integrating supporting structures, enabling performance comparisons with and without a support.
Key Takeaways
- AN-SOF’s project merging feature allows for combining wire structures from different projects, enabling comprehensive antenna system analysis.
- Importing wires simplifies the evaluation of combined structures’ electromagnetic response and facilitates comparison with individual responses.
- Supporting structures for antennas, such as towers and poles, can be saved as separate template files and later imported and merged with an existing antenna design.
Wires can be imported into AN-SOF from another AN-SOF project, allowing wire structures from different projects to be seamlessly merged into a new project. When a project is saved, a file with the extension .wre is also saved, containing the geometrical description of the wires. To import wires into a project, simply navigate to the File menu > Import Wires > AN-SOF Format, and select the .wre file you wish to import.
This feature enables the analysis of the electromagnetic response of an antenna and its supporting structure separately, and then combines them into a new project to analyze the response of the entire structure.
For example, one can model a directional antenna such as a Yagi-Uda or a Log-Periodic Dipole Array (LPDA) and analyze its performance in terms of antenna gain and bandwidth. This model can be saved as an individual project complete with the corresponding simulation results (input impedance, VSWR, gain, front-to-back ratio, etc.). In another project, one might have a broadcast tower and wish to install the directional antenna (Yagi or LPDA) using the tower as its supporting structure. In this case, the tower geometry can be imported into the directional antenna project, allowing a simulation to evaluate the changes in antenna gain and bandwidth due to the electromagnetic interaction with the tower. Figure 1 illustrates a tower and an LPDA in separate projects within the AN-SOF workspace, as well as both combined into a single project.
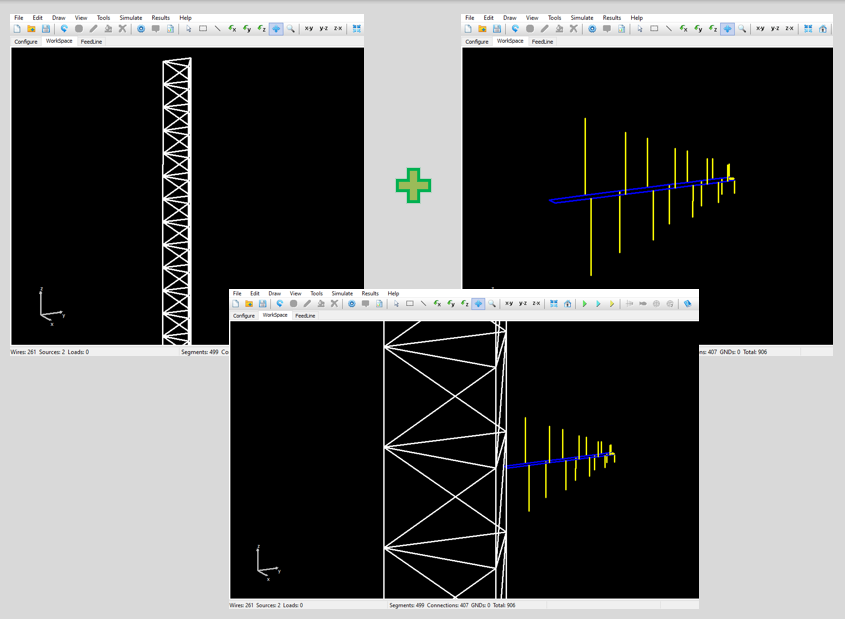
It’s important to note that electromagnetic responses, both near and far fields, do not simply add up because of the mutual interactions between the elements of each structure. Therefore, the calculation must be rerun for the combined structure.
Tip:
Antenna supporting structures, such as towers or poles, can be saved in separate project files as templates. These templates can be imported into other projects when needed, with the aim of evaluating the change in performance of an antenna design with and without the supporting structure.
When importing a structure into another project, it is often necessary to rescale it, reposition it, or rotate it around a specified axis. These operations can be easily performed using the Scale, Move, and Rotate functions available in the Edit menu.
An illustrative example can be found in our knowledge base: two 10 MHz dipole antennas mounted on a ship, as shown in Fig. 2. The ship model is stored separately, with seawater modeled as a PEC ground plane in AN-SOF due to its high conductivity at 10 MHz. The ship’s structure is grounded to simulate contact with water. Click the button below Fig. 2 to download the ship model file in AN-SOF format (.wre).
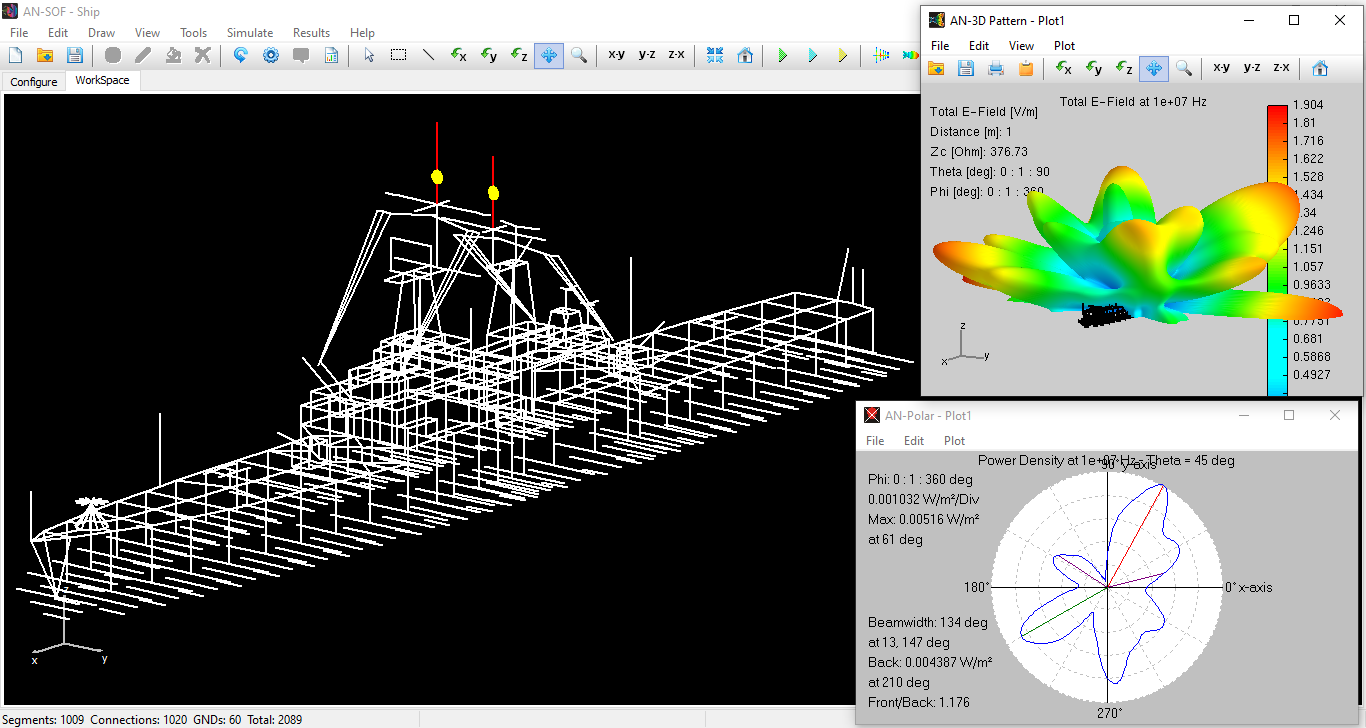
With AN-SOF’s importation feature, merging multiple projects is straightforward, making it a valuable tool for leveraging previously created structures and maintaining a library of antenna supporting structures as templates to be used when needed.
See Also:

About the Author
Tony Golden
Have a question?
